 |
 |
The HMC6352 is an I2C digital compass without tilt compensation. This makes it cheap - you can buy a breakout board from SparkFun for $35. The problem is that when you tilt the sensor the results a pretty unpredictable. A comparable compass breakout board with tilt compensation (like the HMC6343) costs $150.
The Registers
The HMC6352 is easy to use. Instead or reading from or writing to some addresses or registers it uses 1 character commands. So, for example 'A' is used to read to current heading in 10th's of a degree (a heading of 1345 would be 134.5 degrees). The slave address is 0x42/0x43, which means the Arduino wire address is 0x21. For more information check out the HMC6352 Datasheet .
I could not get the Bus Pirate to work, maybe the timing is a little off. The Arduino works just fine.
Arduino Code
All the code be downloaded from here.
This code does not do anything fancy, it just reads the heading over and over. For a real application it would be better to wake up the module, read the value, and put it back in sleep mode.
#include <Wire.h>
// Shift the device's documented slave address (0x42) 1 bit right
// This compensates for how the TWI library only wants the
// 7 most significant bits (with the high bit padded with 0)
// This results in 0x21 as the address to pass to TWI
const int HMC6352Address = 0x42 >> 1;
int ledPin = 13;
boolean ledState = false;
byte headingData[2];
int i, headingValue;
void setup()
{
I2C_powerPins(3, 2);
delay(100); // wait for things to stabilize
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as output
Wire.begin();
}
void loop()
{
// Flash the LED on pin 13 just to show that something is happening
// Also serves as an indication that we're not "stuck" waiting for TWI data
ledState = !ledState;
digitalWrite(ledPin, ledState ? HIGH : LOW);
// Send a "A" command to the HMC6352
// This requests the current heading data
Wire.beginTransmission(HMC6352Address);
Wire.send("A"); // The "Get Data" command
Wire.endTransmission();
// The HMC6352 needs at least a 70us (microsecond) delay after this command. Using 10ms just makes it safe
delay(10);
// Read the 2 heading bytes, MSB first
// The resulting 16bit word is the compass heading in 10th's of a degree
// For example: a heading of 1345 would be 134.5 degrees
Wire.requestFrom(HMC6352Address, 2); // Request the 2 byte heading (MSB comes first)
i = 0;
while(Wire.available() && i < 2) {
headingData[i++] = Wire.receive();
}
headingValue = (int)headingData[0] << 8 | headingData[1]; // Put the MSB and LSB together
Serial.print("Current heading: ");
Serial.print(headingValue / 10); // The whole number part of the heading
Serial.print(".");
Serial.print(headingValue % 10); // The fractional part of the heading
Serial.println(" degrees");
delay(500);
}
void I2C_powerPins(byte pwrpin, byte gndpin)
{
DDRC |= _BV(pwrpin) | _BV(gndpin);
PORTC &=~ _BV(gndpin);
PORTC |= _BV(pwrpin);
}
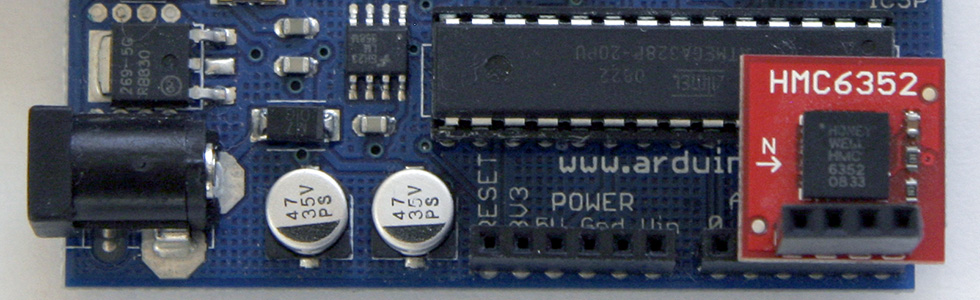
I used the nice wire layout of the SparkFun breakout board to power the module with the analog pins 2 and 3. If you don't do this, you should remove the two lines from the code:
I2C_powerPins(3, 2); delay(100); // wait for things to stabilize